UNDP/UNCDF joint offer on digital financing of the SDGs
In 2018, the UN Secretary General established the UN Secretary-General’s Task Force on Digital Financing of the SDGs (DFTF), which was part of his broader Roadmap for Financing the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development: 2019-2021. The mandate of the DFTF was to catalyze and recommend ways to harness digital financing to accelerate the financing of the SDGs. UNCDF hosted the secretariat of this task force that brought together 17 leaders from finance, technology, policy, regulation and international development. Through their work, the leaders in the DFTF engaged in dozens of countries with hundreds of experts and institutions over an 18-month period.
On 26 August 2020, UN Secretary-General António Guterres, together with DFTF Co-Chairs Achim Steiner and Maria Ramos, launched the report of the DFTF: People’s Money: Harnessing Digitalization to Finance a Sustainable Future.
The DFTF’s findings point to digital disruption as an historic opportunity to reshape finance. Digitalization has a transformative impact by empowering people as savers, lenders, borrowers, investors, and taxpayers. The DFTF focused on how digitalization can support the development of a citizen-centric financial system that supports peoples’ priorities, collectively represented by the SDGs.
After the release of the DFTF report in mid-2020, UNDP and UNCDF have been working together to implement its recommendations and synthesize its work into actionable offers. To help steer developments and seize upon this historic opportunity, the DFTF report outlined an Action Agenda with a set of recommendations for Member States to take forward.
The Action Agenda outlined three interconnected areas of work, namely (i) strengthen inclusive international governance of digital financing, (ii) build the foundations for sustainable digital financing ecosystems, and (iii) advance and implement large-scale digital financing solutions (so-called catalytic opportunities) to trigger systemic changes. The DFTF highlighted that the UN-System with its diverse expertise and facilitating power needs to support Member States to implement the Action Agenda.

Figure 1: DFTF Action Agenda
To this end, UNDP and UNCDF have combined forces to utilize each agency’s complementary expertise to support Member States in advancing key recommendations and materialize large scale opportunities, through the creation of a Joint Offer on Digital Financing for the SDGs. This joint offer is constituted in three complementary service offers: (1) Dialogue on Global Digital Finance Governance (UNCDF Inclusive Digital Economy Unit Workstream 1: Policy & Regulation), (2) SDG-anchored Digital Finance Ecosystem (SDFE) Assessments (UNCDF Inclusive Digital Economy Unit Workstream 2: Infrastructure), and (3) SDG Digital Finance Accelerator (UNCDF Inclusive Digital Economy Unit Workstream 3: Innovation).
The expected results of this programme are developing countries able to employ, leverage and govern digital technologies which support achievement of the SDGs.
1. Dialogue on Global Digital Finance Governance
The Dialogue was established to explore the nexus of BigFintechs and sustainable development. Its goal is to catalyse governance innovations that take greater account of the SDG impacts of BigFintechs and are more inclusive of the voices of developing nations. To this end, the Dialogue has produced a series of Technical Papers that bring new, complementary perspectives on these issues. The papers have been drafted by commanding experts in the field and have been peer-reviewed by leading institutions and academics.
The findings are packaged into three thematic areas:
SUMMARY PAPER
Theme 1: BigFintechs and their impacts on sustainable development
Theme 2: Corporate governance innovations
Theme 3: BigFintechs and international governance, policymaking and the SDGs
The Dialogue on Global Digital Finance Governance is hosted by the Swiss and Kenyan Governments and stewarded jointly by UNDP and UNCDF.
2. Develop SDG-anchored Digital Finance Ecosystems (SDFE)
The second service offer is providing support to Governments that would like to harness the potential of their digital finance ecosystems to finance their national priorities. This offer builds on UNDP’s expertise in national planning processes and UNCDF’s engagement in all aspects of digital finance. Governments are increasingly operationalizing their commitments to Agenda 2030 through National Development Plans and other sustainability-focused strategies, plans and frameworks. Nearly all national development strategies (90%) approved from 2015 onwards reference the 2030 Agenda and/or the SDGs.* Yet, most national strategies do not detail how they will be financed.** The UN-system and the European Union (EU) are therefore supporting Governments to delineate how national plans will be financed through Integrated National Financing Frameworks (INFFs) - a mechanism to help align plans, policies, and financing flows to development targets. As developing countries are facing constrained availability of Overseas Development Assistance and concessional loans, high foreign exchange costs, interest rate costs of foreign debt, and increasing financing needs in recovering from the socio-economic impact of COVID-19, digital financing holds great potential to mobilize sufficient financing for sustainable development priorities.
However, there exists a disconnect between, on the one hand, national planning processes related to financing of national developments plans and sustainable development priorities and, on the other hand, policies on digital financing and market developments. As the DFTF points out, Governments have largely pursued digitalization of finance as a means to modernize and expand reach of financial services, separately from broader sustainable development priorities.*** Yet, aligning these two siloed areas will catalyze significant financing for national sustainable development priorities while steering the development of a more inclusive and citizen-centric digital financing ecosystem. Therefore, to harness this potential, UNDP and UNCDF are jointly supporting Governments in linking their digital financing policy planning with national planning processes for the SDGs through (i) an assessment and diagnostic process of the level of development and SDG-alignment of the domestic digital financing landscape and (ii) the creation of SDG digital financing strategies. Such work may optimally be situated in the context of an INFF-process but can also be undertaken outside of the INFF. The process will begin with an SDG–anchored Digital Finance Ecosystem (SDFE) Assessment that is undertaken with a SDG lens. The assessment includes indicators from UNCDF’s Inclusive Digital Economy Scorecard, and adds two additional layers: evaluating the current state of a country’s digital finance ecosystem and understanding the fintech industry and whether it is evolving with a SDG-lens. Once the SDFE is completed, it can, for example, be used in the context of the Development Finance Assessment (DFA) which is the initial step undertaken under an INFF.
Currently, UNDP and UNCDF are piloting SDFE assessments in Namibia, Bangladesh and Uganda with tools, guides, and lessons learned to be generated and shared with other COs/Governments that wish to bolster their SDG financing plans through digitalization.
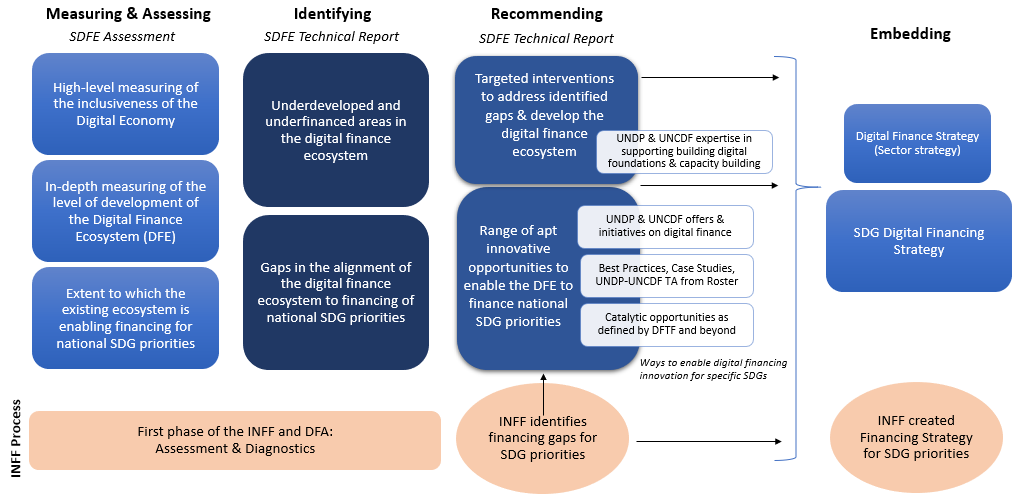
Figure 2: Sequencing of integrating digital financing into the INFF-process through the SDFE Assessment
Under this service offer, UNDP/UNCDF team will continue with the following initiatives:
- Support Governments in assessing domestic digital financing ecosystems to identify targeted interventions that may enable financing for national SDG priorities.
- Support development of Government-owned SDG Digital Financing Strategies.
- Support embedding digital financing considerations, such as through assessments and SDG digital financing strategies, into INFF processes.
3. SDG Digital Finance Accelerator
In recent years, the financing landscape has considerably changed and increasing digitalization across real economy sectors has created new pathways for development finance. Inspiring examples are emerging, such as in Bangladesh, on how digital finance innovations can be harnessed to channel domestic micro-savings into investments in green sustainable infrastructure, with the potential to bridge the USD12.5bn annual need in infrastructure development, or in Zimbabwe where the world’s first stock exchange was launched that draws on automatically generated payments data from businesses to provide robust credit ratings for debt and equity financing for fast growing SMEs. These examples of how digitalization can transform development finance, mobilize new financial flows and empower citizens to become development actors are what the third service offer will focus on. UNDP/UNCDF team will help to identify break-through innovations which deploy digital technologies to empower citizens themselves to help reach the SDGs, and use its global platform to capture knowledge, document case studies, provide tools, templates, and experts.
Endnotes:
* IATF, Financing for Sustainable Development Report 2020 (2020), p. 99
** Ibid.
*** DFTF, People’s Money: Harnessing Digitalization to Finance a Sustainable Future (2020), p 48
Stay Connected
GET THE LATEST UPDATES TO YOUR INBOX
