Inclusive Digital Economies
Financial inclusion is not the end goal, it is a means to multiple ends
Meaningful digital financial inclusion must enable those with low income to meet their daily needs and improve their skills, productivity, and marketability in the digital age. UNCDF strives to ensure that everyone can access, use and benefit from a broad range of essential services built on digital platforms and that no one is left behind.
Leave No One BehindDigital financial inclusion is directly contributing to the emergence of digital economies, and vice versa
The past two decades have seen a phenomenal change in the adoption of mobile and digital technology in emerging markets. Around 20% of the population in the least developed countries (LDCs) is using mobile internet and 1.6 billion people have a registered mobile money account (GSMA SOTIR 2023).
Yet a large portion of the population remains unconnected
29%
of adults
worldwide lack access to mobile internet services and skills (GSMA SOMIC 2022).
1.4 billion
of the adults
lack access to safe, secure, and affordable financial services (Findex 2021).
And these unconnected (94%) disproportionally live in low and middle-income countries and are likely poorer, less educated, older, rural, and female.
Inclusion in the digital era isn't guaranteed
Technology is neutral but also increases exclusion depending on how it is deployed. Adoption of innovation and technology depends on users' digital skills and perceived value of digital services. Bridging the digital divide requires user-centric design and tailored services to impact people’s lives and livelihoods positively.
Our goal is to empower millions of people by 2024 to use services daily that leverage innovation and technology and contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). To achieve this vision UNCDF uses a market development approach and continuously seeks to address underlying market dysfunctions that exclude people living in the last mile.
Inclusive Digital Economies for the Sustainable Development Goals
A breakthrough publication that combines insights from across UNCDF along with expert contributions from over a dozen organizations on the future of digital economies and how to make the digital transformation inclusive.
DownloadBuilding the rails for inclusive digital economies
UNCDF leverages digital finance in support of the SDGs to realize its vision of advancing inclusive digital economies.
As a hybrid development finance institution and development agency, UNCDF uses a combination of capital and development instruments to promote digital finance and inclusive digital economies in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific.
Our Approach
UNCDF's approach focuses on four key building blocks, also termed workstreams: skills, innovation, infrastructure, and policy & regulation, to form the foundation of an inclusive digital economy.
Skills
providing customers with the knowledge, and skills, to access and use digital tools and financial products in a meaningful way.
Learn MoreInnovation
developing business models and services that address customer needs across various sectors (finance, agriculture, health, education, energy).
Learn MoreInfrastructure
strengthening the digital rails (device ownership, mobile networks, distribution network, access to energy, digital ID) and reducing the digital divide.
Learn MorePolicy and regulation
developing digital economies characterized by inclusive policies and regulations that enable access to and usage of digital services.
Learn MoreWith an emphasis on data, we adopt a focused strategy, seeking to build inclusive digital economies that work for all.
The Inclusive Digital Economy Scorecard (IDES) is a strategic performance and policy tool that has been developed to support countries in better understanding and monitoring the status of their digital transformation, with a view to helping them make it more inclusive.
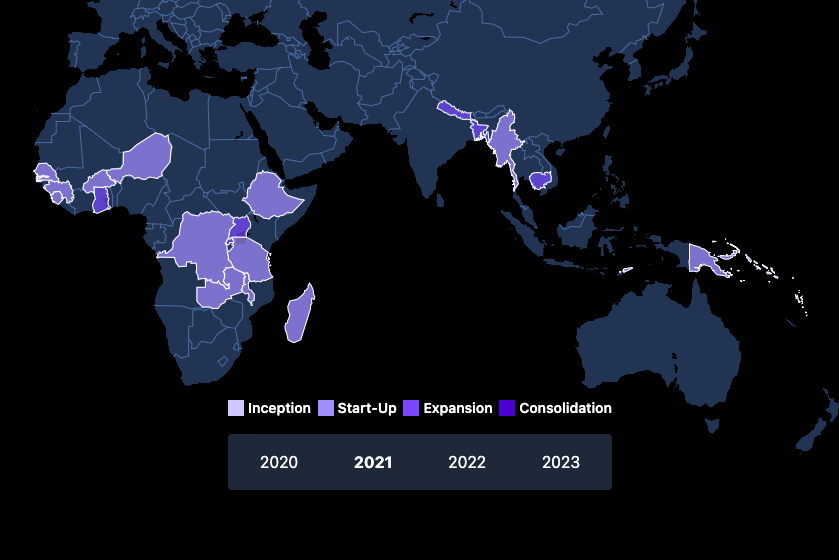
UNCDF plays the role of facilitator in the countries
where we operate
The digital era has excluded billions of citizens, particularly from vulnerable demographics. UNCDF leverages its capacity to bring together the public and the private sectors and emphasizes the need to empower customer segments that are often prevented from accessing digital technology and innovation due to social norms, societal status, and limited resources and digital skills.
UNCDF prioritizes low-income populations that are marginalized and excluded, specifically:
+
Women
+
Youth
+
Migrants
+
MSMEs
+
Refugees
+
Farmers
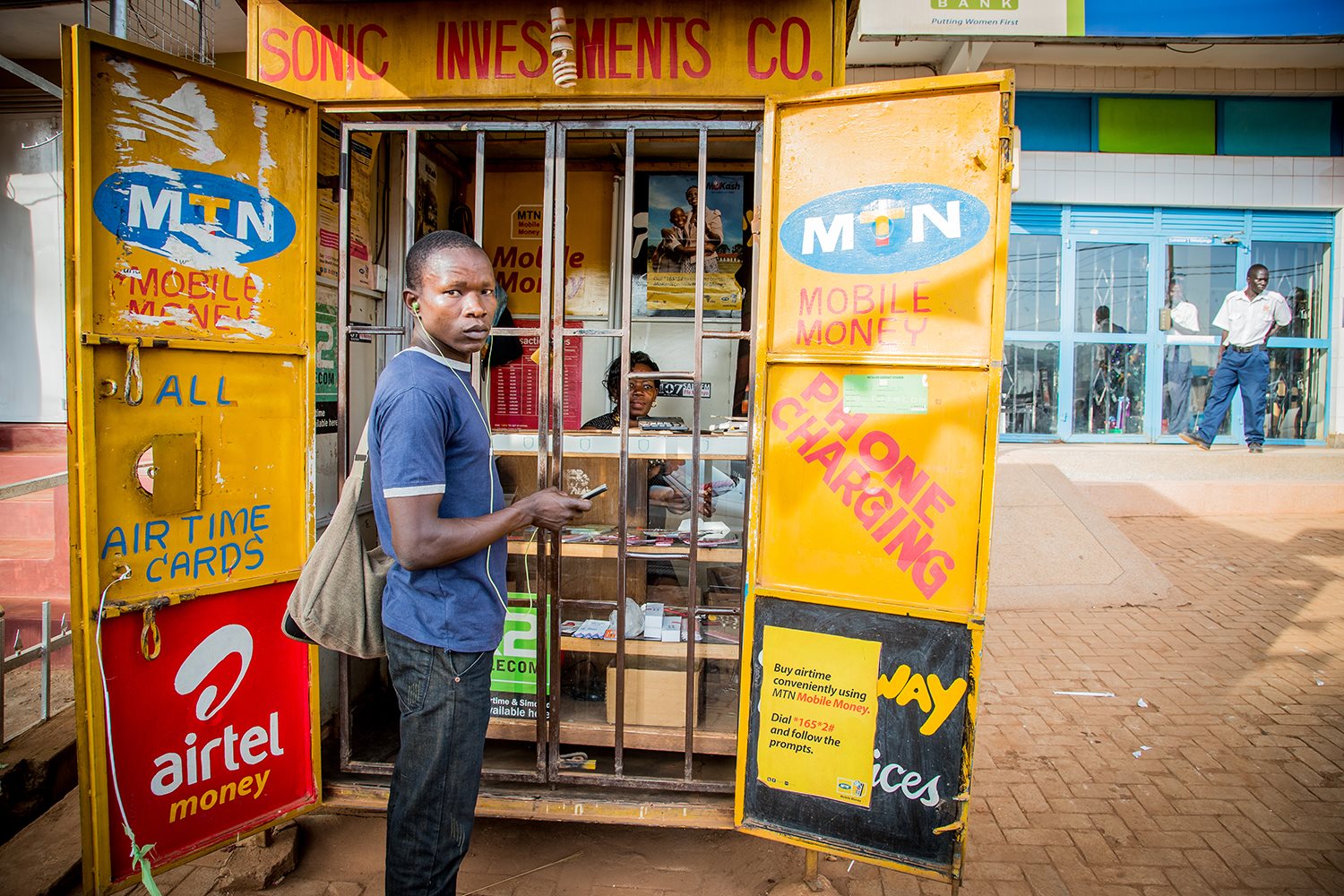

An Experienced Hand in Digital Financial Inclusion
With previous digital finance initiatives dating back to 2004, the success of past and present UNCDF interventions is measured by the millions of people now having access to digital skills and digital financial services in Africa, Asia and the Pacific.
Our team has a unique experience in accelerating digital finance usage in key markets built over the years making sure impactful services reach individuals in the last mile. Some of our previous interventions include Mobile Money for the Poor, MicroLead, YouthStart and CleanStart. The success of these programmes has led to the development of UNCDF’s global strategy, Leaving No One Behind in the Digital Era.
For more initiatives contributing to inclusive digital economies visit:
Better Than Cash Alliance
A partnership of governments, companies, and international organizations that accelerates the transition from cash to digital payments in order to help achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Learn MoreMaking Access Possible
The MAP diagnostic approach builds a picture of market demand based on household and individual income, economic activity, and current usage of financial services within a diverse array of countries and local contexts.
Learn MorePacific Insurance and Climate Adaptation Programme
The PICAP programme aims to improve the financial preparedness and resilience of Pacific people towards climate change and natural hazards.
Learn MoreEnergy
The CleanStart programme supports low-income households and MSMEs to jump-start their access to clean energy through microfinance.
Learn MoreDigital Finance for Resilience
The DFS4Res aims to deploy digital finance solutions at scale to deepen financial inclusion and accelerate economic recovery from COVID-19 to make economies and societies more resilient to external shocks.
Learn MoreMigrant Money
Migrant Money works to address the income volatility, uncertainty, and financial insecurity of migrants. Financially resilient migrants allow for financially resilient economies, locally and globally.
Learn MoreStay Connected
GET THE LATEST UPDATES TO YOUR INBOX